Instructions
Q&A (0)
Notes (0)
Resources (0)

Saving Progress...
Resources
There are no resources for this lesson.
Notes can be saved and accessed anywhere in the course. They also double as bookmarks so you can quickly review important lesson material.
In this lecture, you are going to learn how to create and manage Group Policy Objects commonly referred to as GPOs.
Now, GPOs contain settings and configurations that can be applied to users or computers that are stored within Active Directory. A Domain can contain several GPOs and you will almost never see a Domain that contains one GPO. It's also important to know that one individual GPO can be linked or applied to multiple OUs simultaneously.
GPOs are often used in a modular sense, meaning that the administrator might create several GPOs or one GPO and apply them to multiple OUs as needed.
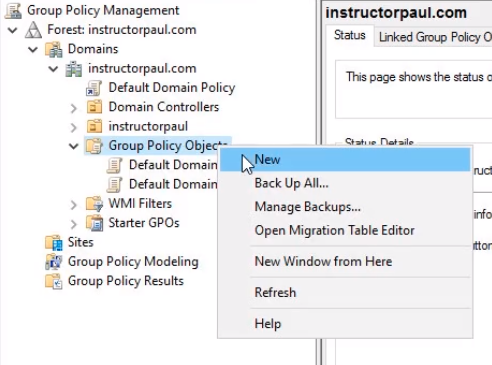
Creating a GPO is very similar to creating a user account within Active Directory. All you need to do is right-click on Group Policy Objects and choose New.
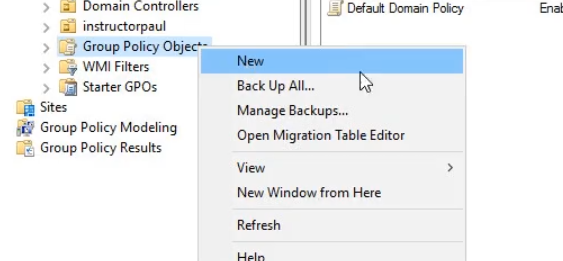
Additionally, you can right-click on your Domain or an Organizational Unit and choose to Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here...
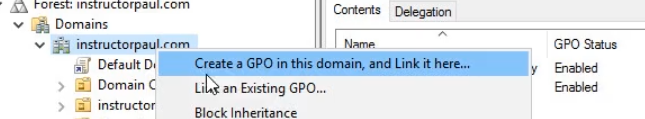
The difference between these two methods is that the Domain/OU option makes a GPO and a Link. This means that the GPO will take effect wherever we create the link.
Let's create a GPO using both methods:
Domain Level GPO
- Right click the domain and choose to Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here...
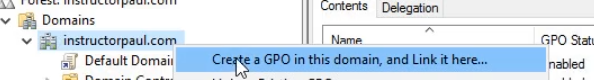
- A New GPO window will appear. Name it Test GPO:
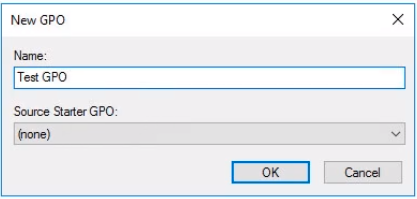
- No starter GPO set. That means that all settings inside the GPO will be not configured.
- Now we can see the link is created, and if we expand GPO objects, we can see our GPO.
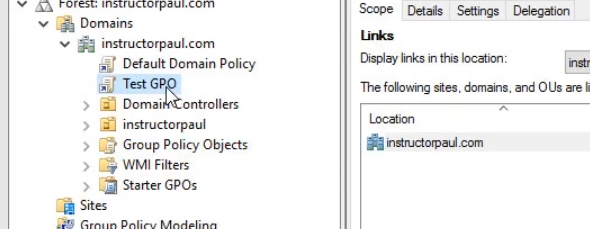
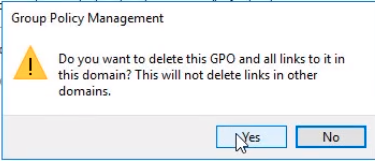
- Right Click on the Test GPO link (under Instructorpaul.com) and choose Delete.
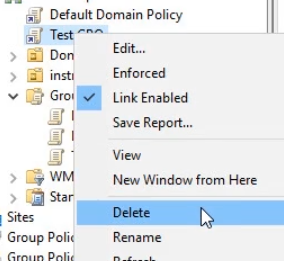
Note the very important pop-up we receive. We only delete the link, and not the GPO itself.
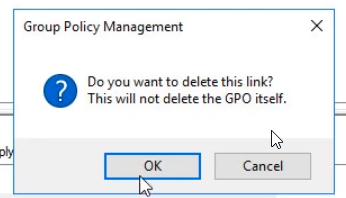
- Test GPO is still listed under Group Policy Objects; we just removed the link.
- Now let's delete the actual GPO. Right click and choose Delete and Yes to the pop-up.
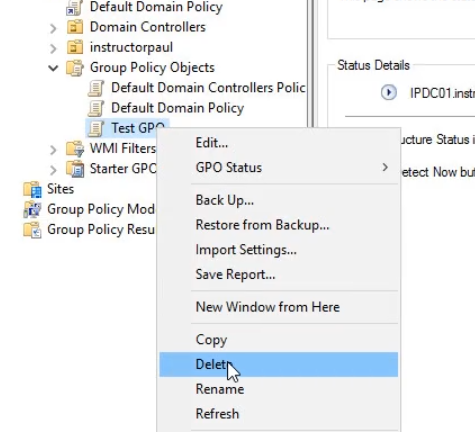
- Now, let's link it, follow the same procedure, this time do it from the Group Policy Objects folder. Right click and select New and follow the same steps as before.
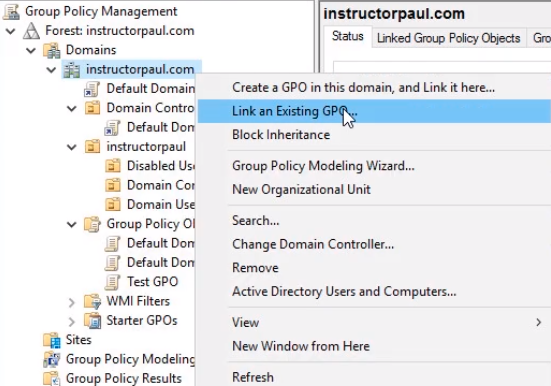
- Now, lets go ahead and link it to the domain : (Right click on instructorpaul.com and select Link an Existing GPO)
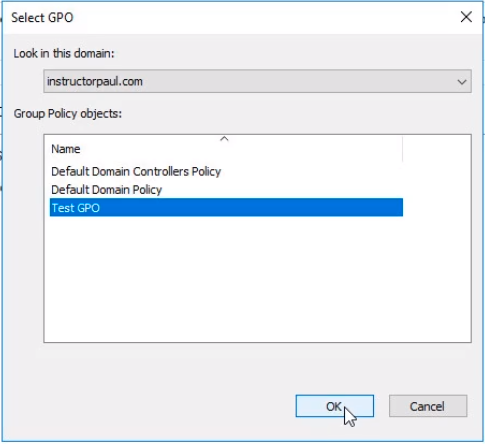
- Now, select our TEST GPO.
- Now we see the Test GPO linked.
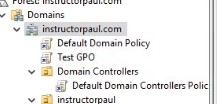
Now let’s delete the link again.
What if we wanted to link the Domain Users + Domain Computers only :
- Right-click the Domain Computers and select Link an Existing GPO.
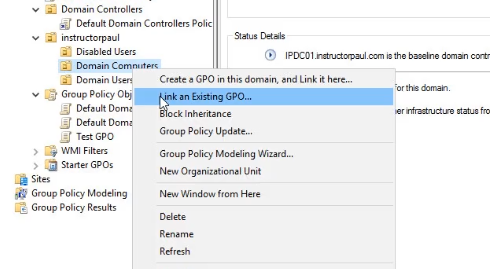
- Now, repeat the same steps for Domain Users.
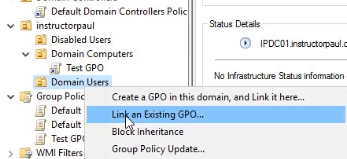
So we go ahead and link it to both OU’s and select our Test GPO. Therefore applying the GPO to both of those OU.
What Options do we have in the GPO? Right-click on Test GPO to see.
- Select Edit (Configure options)
- Enforced (Force the GPO)
- Enable and Disable (Only Disables, does not delete as we had done previously)
- Pull a report of the current GPO
- Delete/Rename/Refresh
Report Example :
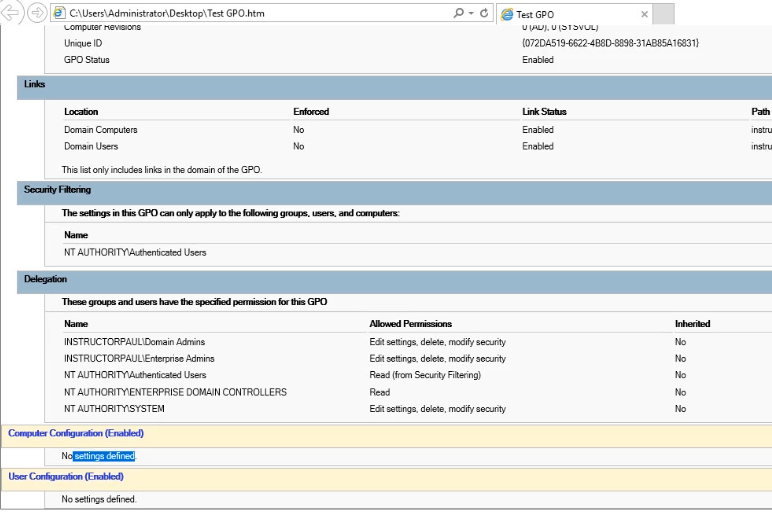
What do we see on the right side window?
Scope Tab :
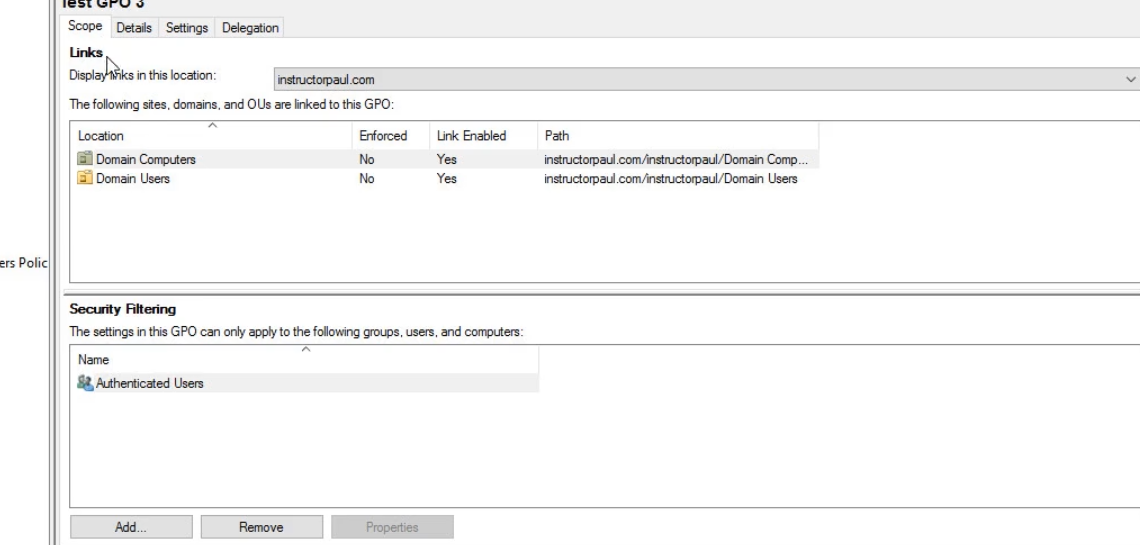
Scope: Where is GPO being applied, we can delete links if required, and also do enforcing if required
Security Filtering: Only apply to certain user types, this allows us to target users and be specific. For example the administrators group:
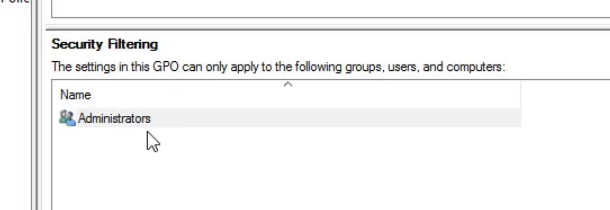
Authenticated Users: Any user account/object that authenticates into the Domain.
WMI Filtering: Further Filtering, only certain OS, for example.
Details Tab :
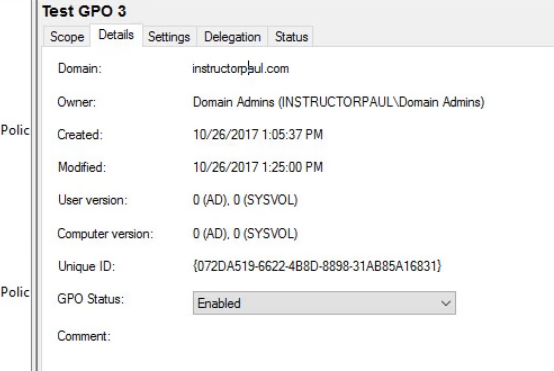
This shows information about our GPO, ID, Status, and any comments.
We can also adjust the settings:
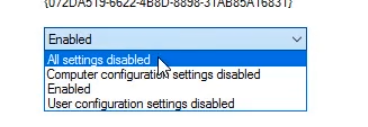
Settings Tab :
Note, by default Internet Explorer blocks this, add an Exception.
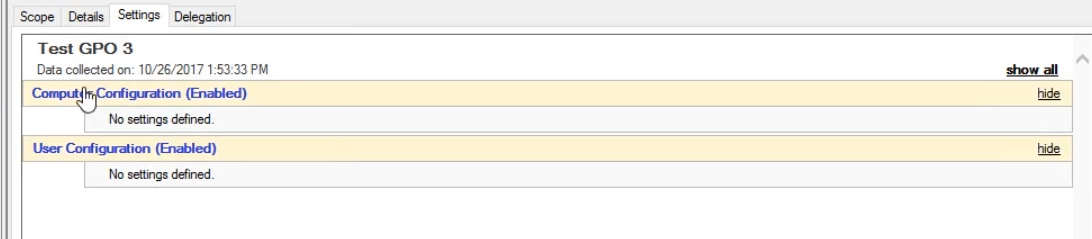
This is a summary of the settings on the Computer/user GPO applied settings.
Delegation Tab :
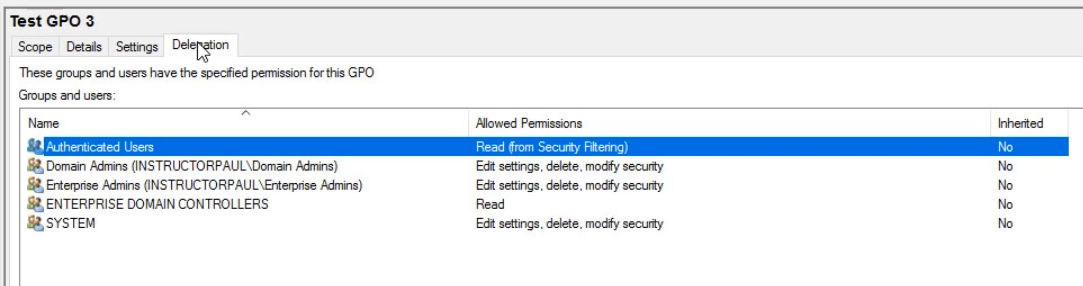
List of users who can read, write, and modify this GPO.
We will explain more of the GPO settings in later videos.


