Installing the DNS Windows Server Role

Full-Access Members Only
Sorry, this lesson is only available to Server Academy Full-Access members. Become a Full-Access member now and get instant access to this and many more premium courses. Click the button below and get instant access now.
Instructions
Q&A (0)
Notes (0)
Resources (0)

Saving Progress...
Resources
There are no resources for this lesson.
Notes can be saved and accessed anywhere in the course. They also double as bookmarks so you can quickly review important lesson material.
In this lecture, I am going to walk you step by step through a Windows DNS server role installation. Before you begin this lecture, you need access to a Windows server preferably with 2016 already installed.
If you want to set up your own lab here are the links that you will need. Here is a link so that you can download Windows Server 2016 https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/evalcenter/evaluate-windows-server-2016 Here is a link so that you can download Virtual Box https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Downloads
DNS Defined
Domain Name System (DNS) provides a standard method for associating names with numeric Internet addresses. This makes it possible for users to refer to network computers by using easy-to-remember names instead of a long series of numbers. In addition, DNS provides a hierarchical namespace, ensuring that each hostname will be unique across a local or wide-area network. Windows DNS services can be integrated with Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) services on Windows, eliminating the need to add DNS records as computers are added to the network.
The best practices in a production environment are:
- The Administrator account has a strong password
- The most current security updates from Windows should be installed.
- It is recommended to Install DNS first then Active Directory.
- Server network cards should be configured with a static IP address.
Update - The question has been asked, “Should I install DNS first or just run the DCpromo wizard and install DNS automatically?” My answer - It’s your choice! You can certainly run the DCpromo wizard and choose the Active Directory Domain Services Role, and install DNS automatically. However, for this lecture, I want my students to know how to install the DNS server role manually. Regardless of whether you choose to use the wizard or install the DNS role manually, be sure to configure a static IP address on the servers NIC, and configure the new domain controllers TCP/IP DNS settings to point at itself as the preferred DNS server. Read on for clarification.
To configure a static IP address on the servers Network interface card, open the server manager which opens by default, or click the Windows start key then select Server Manager.

In the left-hand panel click local server. In the right-hand panel double click on any interface card.

Double click on the Ethernet card that will be configured. Click properties, then highlight Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4), then select properties.
After configuration, the properties screen should look similar to this screen
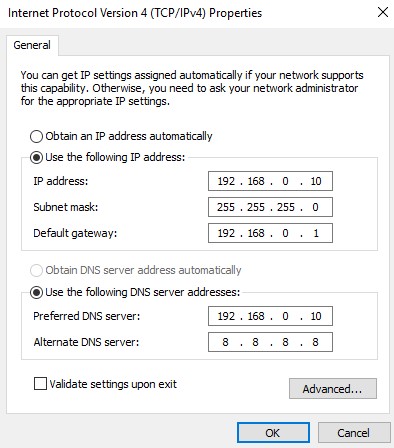
The server IP address is 192.168.0.10. The .10 (the last octet) is the address of the Host (which is your computer).
The subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 is a standard subnet mask for a class C network.
The default gateway is your router’s IP address.
I use the server's own IP address for the preferred DNS address, and normally I set the Alternate DNS server address to another Domain Controller. In this case, I set the IP address to Google's DNS server.
The preferred DNS server is the device's “first choice when making DNS requests. Alternate servers are only used when the primary DNS server does not respond. The main benefit for two DNS servers is that if one DNS server has failed, this does not prevent users from accessing web pages. It allows devices to continue resolving addresses even if the primary server is down.
The following pages contain a step-by-step instructions on how to install the
Windows DNS
- Next open Server Manager – Select Add roles and features in yellow.

Server Academy Members Only
Sorry, this lesson is only available to Server Academy Full Access members. Become a Full-Access Member now and you’ll get instant access to all of our courses.



The video quality option for this video is only 240p, its hard to clearly see the screen, can this be resolved?
Hi Emem Ndon
Emem Ndon
Thanks for reporting. We have notified Paul about it so he can update the video resolution.
Ricardo